Music used to be about people in a room with instruments, voices, and feelings. Now, artificial intelligence is offering a fresh way to make, mix, and even listen to music. From chart-topping artists to hobbyist creators, AI-generated music is sparking conversations everywhere. Programmers and musicians aren’t the only ones paying attention—producers, app developers, indie artists, and fans are curious as well.
AI-generated music comes up in debates about creativity, toolmaking, and emotional impact. Some see it as pure innovation, while others worry about the future of human musicians. No matter how you feel, AI in music keeps growing. Let’s break down what makes this technology tick, who uses it, and what makes it so fascinating—even a little controversial.
How Does AI-Generated Music Work?
Imagine teaching a computer to write a song the way you’d teach a teenager to bake cookies. You’d give it examples, basic instructions, and maybe a few playlists. That’s how AI learns to make music—by studying loads of data, recognizing patterns, and creating something new from what it absorbs.
AI systems use algorithms and data to “compose” in lots of formats:
- MIDI-based music: AI arranges notes, chords, and timing (think sheet music for computers).
- Audio-based generation: AI builds real sounds, like singing voices, instruments, and even complex soundscapes.
These systems don’t just remix old tracks. They can produce original melodies, entire backing tracks, or even sing in the style of famous artists. Some AIs aim to imitate a band or genre (like classic jazz or modern EDM), while others experiment with new, unusual combinations.
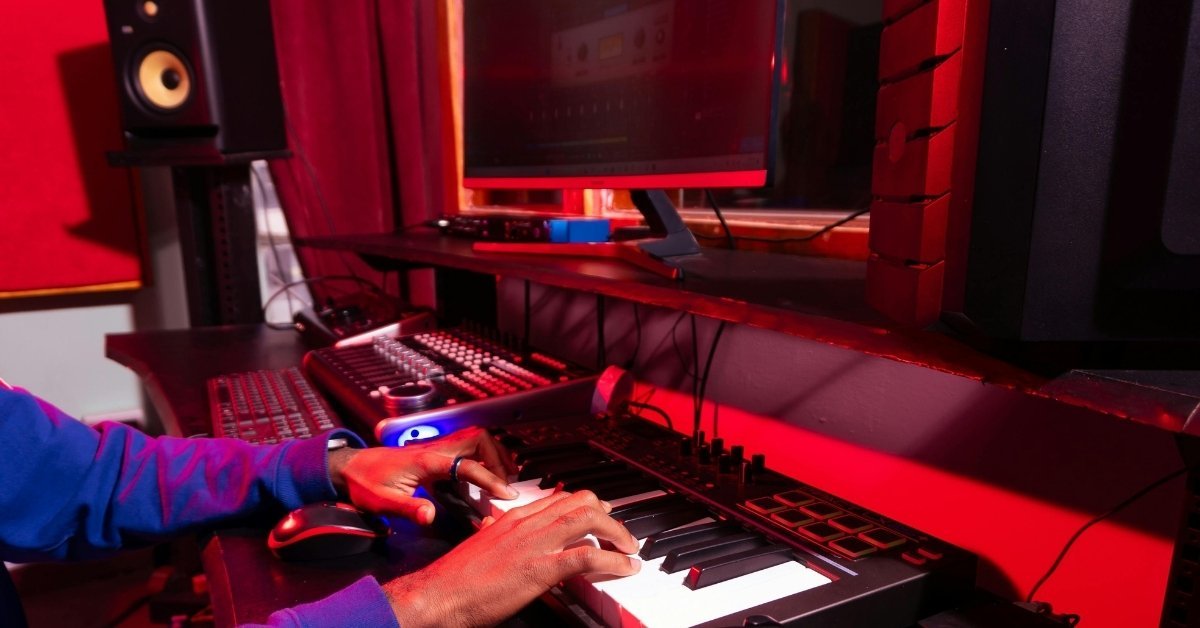
 Photo by RDNE Stock project
Photo by RDNE Stock project
Key Technologies Powering AI Music
Behind every AI-made track, you’ll find stacks of technical ideas—some sound complicated, but many are just digital tools tweaking or learning from musical patterns. Here are a few technologies making AI-generated music possible:
- Deep learning: Think of this as a digital ear learning to tell the difference between sounds, melodies, and textures.
- Recurrent neural networks (RNNs): RNNs are great at handling things that happen in sequences, making them perfect for music that plays out over time.
- Long short-term memory networks (LSTMs): Popular for keeping track of things like rhythm and melody over many notes or bars, so songs don’t sound random.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs): Two digital models in a “duel”—one tries to make convincing music, while the other tries to spot flaws, pushing each other to improve.
- Transformer-based models: Tools like MuseNet and Music Transformer use sophisticated pattern prediction to compose longer, more intricate pieces.
Symbolic (score-based) generation is about writing digital sheet music, while audio-based generation creates finished sound files. Symbolic systems are lighter, faster, and good for creating base tracks; audio-based tools can closely imitate real instruments and voices, adding depth and realism.
Real-Life Examples and Popular AI Tools
Every few months, new AI music tools pop up, raising the bar higher. Some apps help humans compose faster, others automate the process completely. A few big names:
- AIVA: This software writes everything from classical scores to pop tunes, and artists use it to help brainstorm or complete projects.
- MusicLM by Google: Famous for its text-to-music feature—type a phrase and the AI spits out a song.
- AI voice cloning: Apps now copy voices so well, you can make an AI “sing” like your favorite artist.
- Automated mastering and mixing: Services like LANDR help polish tracks with AI.
If you’re curious about more options, there are showcases and lists for the best AI music generator software and some of the most popular AI music platforms. Each tool has its own uses, from composing to generating, collaborating, or just experimenting.
Impact and Debates Around AI-Generated Music
AI-generated music is shaking up the way people think about art, creation, and even ownership of sound. Artists might use these tools as creative partners, sketchpads, or even full-on collaborators. For producers and small studios, AI promises faster turnaround and lower costs. Fans get easier access to custom tracks, playlists, and new genres.
But excitement comes with debate. Should software be allowed to “cover” a human singer’s voice? Are we losing emotional depth when a song is written by a machine? And where do copyright rules fit in?
Copyright, Ethics, and Emotional Authenticity
Ownership over AI-generated music isn’t always clear. If a person prompts an AI, should both get credit? Laws in many places haven’t caught up, making it tricky for artists and platforms to sort out payment and rights. You can dive deeper into challenges like these and see how AI sites are helping musicians navigate tricky situations.
Emotional authenticity is another hot topic. Some critics argue that computer-generated tracks can be technically perfect but lack the feeling or imperfections that make music special. Others say that emotion comes from the listener’s experience, not just the creator’s intent. There’s no simple answer, but it’s giving rise to great discussions about what music really means.
Bias in AI is also part of the conversation. Sometimes, if training data is skewed, the AI may copy stereotypes or miss entire genres. This challenge forces AI developers and musicians to keep a close eye on quality and diversity.
Where AI-Generated Music Fits in the Creative World
AI music shows up everywhere: live shows, indie albums, Spotify playlists, and TikTok trends. On stage, it backs performers with real-time accompaniment or remixes. In the studio, AI can quickly sketch out harmony, lyrics, and even finished vocals. Streaming platforms might use AI to recommend, mix, or even generate entirely new content.
The creative process is shifting. Some musicians embrace AI as a tool that boosts their workflow, singing or playing alongside digital bandmates. Others worry about losing control or audience trust. Fans are still getting used to the idea, but as AI tools improve, listeners care more about the song’s impact than its origin.
No one knows exactly where the mix of human and machine will go. As the industry adapts, the relationship between technology and creativity will keep stretching and changing.
Where We Go From Here
AI-generated music is changing the meaning of creativity in fun and unpredictable ways. As machine-made songs fill up playlists and studios, people keep asking fresh questions about what makes music real, honest, or original. I see these tools as partners, not rivals, for human artists. The technology can free up time, spark ideas, or unlock sounds we never imagined.
Plenty of debate lies ahead. But whether you’re a fan, a critic, or a creator, one thing stays true: music keeps evolving. When I use AI for inspiration or production, I still find that the best songs are the ones that connect, surprise, or move me. The future of music may sound different, but its heart—human or AI—will always matter.
Read more: Best AI Music and Voice Generators in 2025